
Choosing the right keywords is a critical part of running successful Google Ads campaigns. Well-selected keywords help your ads reach the right audience, improve your click-through rates, and make better use of your advertising budget. This process involves understanding how potential customers search, identifying relevant keywords and phrases, and organizing them in a way that maximizes ad performance.
By applying keyword research techniques, using match types correctly, and avoiding irrelevant traffic through negative keywords, you can improve the effectiveness of your campaigns and attract users who are more likely to be interested in your products or services.
Use Google Ads Keyword Planner for Fresh Ideas
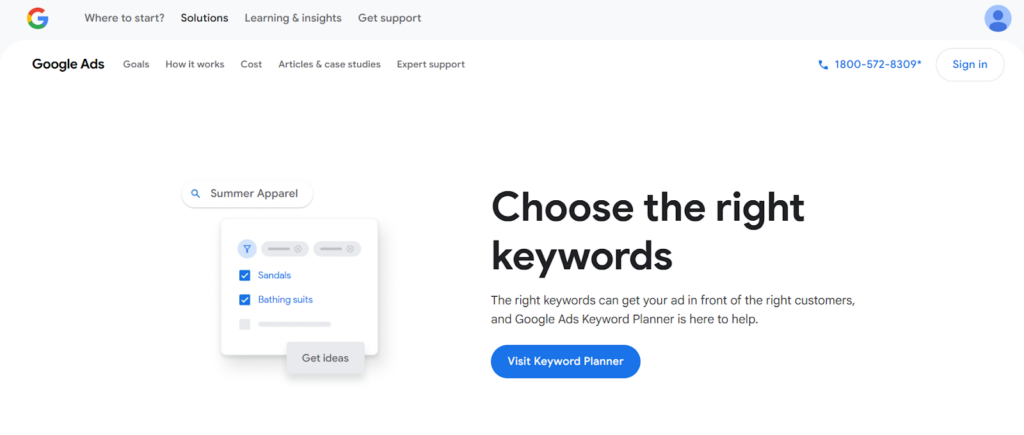
Expand your keyword list by using the Google Keyword Planner tool. Enter a product, service, or webpage, and the tool will suggest related keywords based on search volume and relevance.
Once you gather ideas, refine your list by selecting the most relevant keywords that align with your ad’s goals. For large campaigns, consider grouping similar keywords into tightly themed ad groups or separate campaigns to improve relevance and performance.
Think Like Your Customers
Before building your keyword list, consider how potential customers search for your products or services. Start by identifying the main categories of your business—these form the foundation of your keyword strategy. For each category, brainstorm terms or phrases your customers are likely to use when searching online.
Include common industry terms, product names, and phrases customers might type into Google. Research variations, synonyms, and popular slang to capture different search behaviors. This approach ensures your keywords align with your customers’ intent, increasing the chances of reaching the right audience.
If you sell men’s athletic shoes, your main category may be “men’s sports shoes”. Expand your keyword list to include words like “men’s trainers,” “men’s running shoes,” and “men’s tennis shoes.” You can also mention particular product or brand names that you provide, such as “Nike Air Max” or “Adidas running shoes”, to attract consumers looking for specific items.
Taking the effort to think like your consumer helps you construct a well-rounded keyword list that attracts more quality visitors to your website.
Identify Effective Keywords and Phrases
When creating your keyword list, prioritize phrases that are specific and directly connected to your products or services. Your keywords should clearly represent what you provide, ensuring that customers looking for such phrases are really interested in your company. This draws in people who are more inclined to click your ad and take action.
Using wide or irrelevant keywords may increase traffic, but it frequently leads to low engagement and wasted investment. Sticking to relevant keywords allows you to target visitors who are truly interested, which improves the overall success of your campaign. To keep on top of changing search trends and client behavior, you should also examine and change your keywords on a regular basis.
Target Specific Audiences with Relevant Keywords
Use precise keywords that align with your ad’s focus if you’re aiming to attract a niche audience interested in a particular product or service. This ensures your ads appear for searches most relevant to your business. However, overly specific keywords could limit your reach.
For example, a sports shoe store might target keywords like “men’s tennis shoes” to attract users searching for that exact product. This increases the chances of your ad showing up when someone looks for tennis-specific footwear or browses related websites.
Expand Your Reach with Broader Keywords
Choose general keyword phrases to reach a larger audience. Broad keywords can cause your ad to appear in a variety of queries, some of which may be unrelated to your business.
Keep in mind:
- General keywords may reduce your ability to target specific customers;
- Competitive terms could increase your ad spend;
- Testing is crucial to see if broader terms deliver the right results.
Ensure that even your broad keywords remain relevant to your business. You can also combine broad targeting with Smart Bidding—Google’s AI-driven system that optimizes your bids based on top-performing searches, regardless of keyword match type.
For example, a large shoe retailer could use a broad keyword like “shoes”. This allows ads to appear for searches covering various footwear types or topics on fashion-related websites.
Add a Website to Generate Better Keyword Ideas
Including your website in keyword research can help produce more keyword ideas by allowing Google’s keyword tools to assess your site content and recommend phrases that are closely linked to your products or services.
This method improves your chances of targeting customers with high buying intent and keeping your advertisements relevant. To get the most out of this feature, make sure your website’s content is comprehensive and optimized. Including well-known brand names in your keywords or ad content may also help build trust and generate more clicks because reputable brands typically communicate quality to potential purchasers.
Use Descriptive Keywords
When using descriptive keywords, it’s best to start with the actual product name and then add relevant adjectives to give more detail and improve ad relevance. For example, begin with “hiking boots” and expand to phrases like “durable hiking boots” or “waterproof hiking boots” to reach users searching for specific features.
Avoid starting your keyword research with general words like “best” or “top” because these terms are too broad and don’t clearly define what the user wants. Relying on phrases like “best hiking boots” without focusing on the product itself can lead to wasted ad spend and attract less relevant traffic.
Use Multiple Related Keywords to Capture More Searches
Using several related keywords helps capture more searches by creating keyword groups with several connected phrases, increasing the likelihood of matching diverse search queries about the same topic and enhancing visibility. For example, grouping terms like “charities to donate,” “charitable contributions,” and “donation opportunities” or “short stories,” “mystery short stories,” and “mystery author” helps you to target the many ways customers search for comparable material.
However, avoid using unrelated keywords or incomplete sentences since it confuses the algorithm and reduces marketing concentration. For example, combining “best charities to donate” with “medical research” or “short stories” with “mystery” and “author” is useless and decreases the relevancy of your advertisements.
Focus on Specific and Relevant Keywords
Choosing targeted and relevant keywords is critical to prevent spending money on clicks that do not result in actual clients. Broad phrases frequently attract random traffic from people who aren’t interested in what you’re offering, and adding unrelated but popular keywords may boost clicks but not improve outcomes.
This not only raises prices but may also harm your brand’s reputation. Instead, focus on long-tail keywords that properly define your products or services. For example, a phrase like “organic vegetable box delivery” targets those looking for just that, but broad phrases like “vegetables” or “delivery” are too ambiguous and may attract the incorrect audience.
Optimize Language and Location Targeting
Adjust language and location settings in your campaign to ensure your ads reach the right audience. Targeting specific regions prevents wasted spend on clicks from users outside your service area.
Location targeting options include:
- Countries;
- Regions or states;
- Cities;
- Custom areas.
This is especially useful for local businesses like restaurants, hairdressers, and retailers, where proximity is essential. To successfully attract local consumers, a bakery in Manchester can configure advertising to display exclusively for individuals searching inside Manchester or neighboring districts.
Include Keyword Variations to Broaden Reach
Customers often search for the same product using different terms. To cover more potential searches, include variations such as:
- Synonyms (shop and store);
- Product names, model numbers, or serial codes;
- Common misspellings;
- Colloquial terms or regional differences;
- Singular and plural forms.
For example, a running shoe store can target keywords like “running shoes,” “trainers,” “sneakers,” “men’s running shoes,” and even common misspellings like “runing shoes” to maximize visibility and attract a wider audience.
Learn How Keyword Match Types Work
Google Ads has a number of keyword match settings that govern how closely a user’s search keywords must match your terms before your ad can display. The punctuation you use while adding keywords influences the match type used.
Broad Match (Default)
With broad match, your ads will display when a user searches for any term that includes your keyword, such as synonyms, related queries, single or plural versions, or variations. No specific punctuation is necessary.
For example, if your keyword is garden design and maintenance, your ad might appear when someone searches garden maintenance, landscape design, or similar terms.
Tip: While this setting increases reach, it may also trigger irrelevant traffic, so monitor performance closely.
Broad Match Modifier (Now Merged into Broad Match but Worth Knowing)
Previously, using a plus sign (e.g., +garden +design) ensured that specific words had to be included in the search for your ad to show. Although Google has integrated this into broad match, understanding this logic helps when setting up keywords and analyzing results.
Phrase Match
Phrase match targets search queries that contain your exact keyword phrase with words before or after it, and you define phrase match by using quotation marks like “garden design and maintenance.” So your ad would show for searches such as urban garden design and maintenance where the full phrase is included but not for design services for gardens and maintenance where the exact phrase is broken.
This makes phrase match a good option when you want more control than broad match while still keeping some flexibility to capture relevant searches.
Exact Match
An exact match provides the most control because your ad appears only when the search query matches your keyword exactly or is a very close variation that retains the same meaning. You set this by using square brackets like [garden design and maintenance], so your ad would show for searches like garden design and maintenance or maintenance and garden design. where the meaning remains the same but not for general terms like garden services.
This helps increase click-through rates as the audience is highly targeted and specifically interested in what you offer.
Group Similar Keywords into Ad Groups
Organizing your keywords into tightly themed ad groups helps Google deliver more relevant ads to potential customers. Each group should focus on a specific product, service, or category. This improves your ad’s relevance and click-through rate.
Example: If you own a shoe store, create separate ad groups:
- Ad Group 1: Running Shoes – keywords like running shoes, running trainers;
- Ad Group 2: Evening Shoes – keywords like evening shoes, dress shoes.
This way, users searching for evening shoes won’t see ads for running shoes, ensuring a better user experience and ad performance.
Exclude Irrelevant Searches Using Negative Keywords
Using negative keywords keeps your advertising from appearing in inappropriate search results, saving you money and enhancing ad performance by targeting the correct audience. Adding a negative sign (-) before a term instructs Google not to display your ad when that word appears in a search.
For example, if you’re targeting “garden design” but don’t want to display advertisements to those looking for gardening books, adding -book will prevent your ad from appearing in such searches. Similarly, if you offer outside plants but not houseplants, adding -houseplants helps to filter away irrelevant traffic.
Negative keywords are also useful when your business name or product terms have multiple meanings. For instance, if your company is called “Apple Tree” and you don’t want to appear in searches related to Apple computers, you can add -Mac or -iPhone to block traffic from people looking for tech products instead of your services.
Using Symbols in Keywords
Recognized Symbols
Using symbols in keywords requires attention since some symbols impact keyword matching while others are ignored or not allowed. Recognized symbols like ampersands (&) and accent marks (á, é, etc.) are treated as distinct characters, meaning keywords such as pavement cafe and pavement café are considered different.
However, certain symbols are ignored and don’t affect how Google matches keywords.
Ignored Symbols (No Impact on Matching)
These symbols can be added but won’t change how Google matches keywords:
- Periods (.) – “Fifth Ave.” is treated the same as “Fifth Ave”
- Plus signs (+) – generally ignored unless part of a known term like “C++”
Invalid Symbols (Not Allowed in Keywords)
Using any of these symbols will trigger an error:
- @ (ampersat)
- \ (backslash)
- ^ (caret)
- , (comma)
- = (equal sign)
- ! (exclamation mark)
- ` (grave accent)
- < > (greater/less than)
- (square brackets) – except for exact match usage
- ( ) (parentheses)
- % (percent sign)
- | (pipe)
- ? (question mark)
- ; (semicolon)
- ~ (tilde)
Special Note on Minus (-) Symbol
The minus (-) symbol works differently based on its placement. Inside a phrase or word, like “well-being,” it is ignored, but if placed directly in front of a word, such as -book, it acts as a negative keyword and prevents your ad from showing when that word appears in a search query. It’s important to avoid adding spaces when using the minus sign since “-red” works as a negative, but “- red” (with a space) might not be recognized correctly. Additionally, some search operators and special characters are automatically ignored by Google.
For example, the site: operator is removed so [site:www.example.com dark chocolate] is treated as [dark chocolate], and logical operators like OR are ignored, meaning OR dark chocolate is read as simply dark chocolate.
Ensure Everything Aligns for Better Performance
Google prioritizes relevance, not just how much you’re willing to spend. Your keywords, ad copy, and landing page content should all work together. The keywords you bid on must be represented in your ad content, which should match the language and offer on the landing page that people arrive at after clicking. This consistency improves your Quality Score, lowers your cost-per-click (CPC), and boosts your ad position.
For example, if your keyword is “running shoes”, your ad should mention running shoes and direct users to a landing page featuring your running shoe collection, not a general homepage.
Conclusion
Choosing the best keywords for your Google Ads campaigns requires careful planning and regular adjustments. By focusing on specific, relevant terms, using keyword variations, applying the correct match types, and excluding irrelevant searches, you can improve your ad performance and reach the right audience.
Regularly reviewing your keyword list, testing different approaches, and ensuring alignment between your keywords, ad copy, and landing pages will help maximize the effectiveness of your campaigns and make better use of your advertising budget.
