Before, when we wanted to search for specific information, we had to be extremely patient. The search engine would match our query with the first similar words it found across millions of web pages, and more often than not, we had to rephrase our request or scroll down and down in the hopes of locating at least one relevant result.
Now, the situation has changed drastically. Any modern search engine does an instant semantic analysis of every query, evaluating its context, intent, and the presence of natural language components. We receive accurate and relevant results, and it’s great for us as consumers.
However, what should website owners and other businesses do to adapt to this new reality? How can they change their SEO strategies to preserve the attention of their target customers? If you’re in this risky boat, don’t worry: once you understand what semantic search is and what it’s based on, you’ll know what to do.
Defining the Concept
What is semantic search? Semantics is a science that studies meaning, and semantic search is an advanced search technique that relies on an AI’s in-depth understanding of the query.
When getting a request, the search engine doesn’t simply look at familiar words in it. It analyzes the relationship between them, assesses the intent behind the user’s question, and considers additional context, like the location, to offer relevant results. As an example, if you’re looking for the “best pizzas,” you’ll see recommendations in your vicinity.
Mechanisms Behind Semantic Search
We’ve established what semantic search is, but how does it work? The whole process involves four core components.
- Natural language processing. NLP is the intersection of artificial intelligence and linguistics that helps search engines recognize the nuances of a spoken language;
- Machine learning. This model analyzes huge volumes of info, including the interactions with the existing users, to imitate how people speak and behave, as well as learn to perform various tasks autonomously;
- Entity recognition. Semantic search enables search engines to recognize word combinations, not just words alone, allowing them to locate a person or a location you’re looking for;
- Context and intent analysis. The mechanisms behind semantic search allow search engines to consider your past browsing history to understand the reasons for your query; they no longer focus on its artificial, limited meaning.
All of these components refine the way our search queries are processed these days, delivering customized and meaningful results.
Benefits of Semantic Search
The progress that the evolvement of semantic search has brought is beneficial in many ways. For one thing, as we’ve already established, online users can now locate the info they want quickly and with minimal frustration. Search engines understand your intentions better, so they know how to meet your needs.
In addition, quality websites have gotten the chance to improve their SEO performance and ranking. Semantic search allows focusing on high-level content relevant to the user’s query, rewarding businesses that seek to deliver quality over quantity.
Finally, people who prefer to use voice search benefit as well since semantic search helps pinpoint short, accurate answers, processing the nuances of a natural spoken language. This results in higher satisfaction every time a user makes a query.
Examples of Semantic Search in Action
What are the examples of semantic search? Let’s consider them based on real-life applications.
Google’s Knowledge Graph
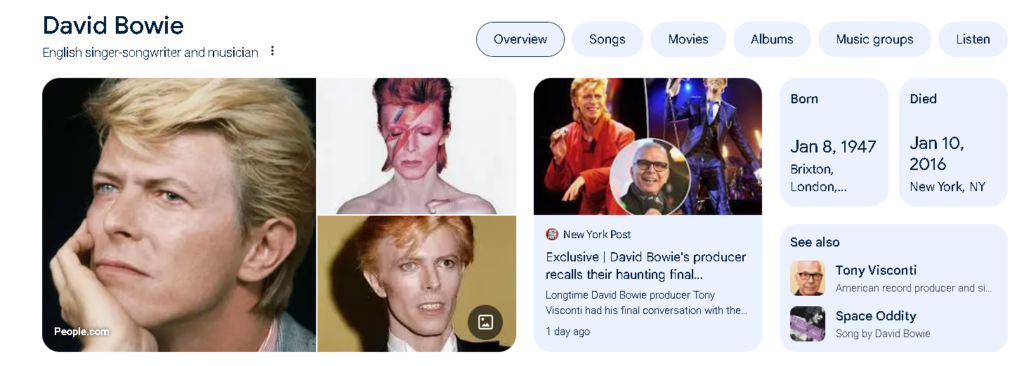
You might have noticed that when you Google something, various web pages are far from the only thing you see. We’re going to use “David Bowie” as an example. Google this name, and here’s what you’ll get:
- A photo of David Bowie with a brief description of who he was;
- Infobox containing his dates of birth and death;
- A YouTube movie dedicated to his biography;
- Queries related to Bowie’s most famous songs;
- A range of his pictures.
You’ll see structured, multi-layered information presented in different mediums, from text to pics and videos. Such a thoughtful and relevant response from the system is the result of a semantic search.
BERT Algorithm from Google
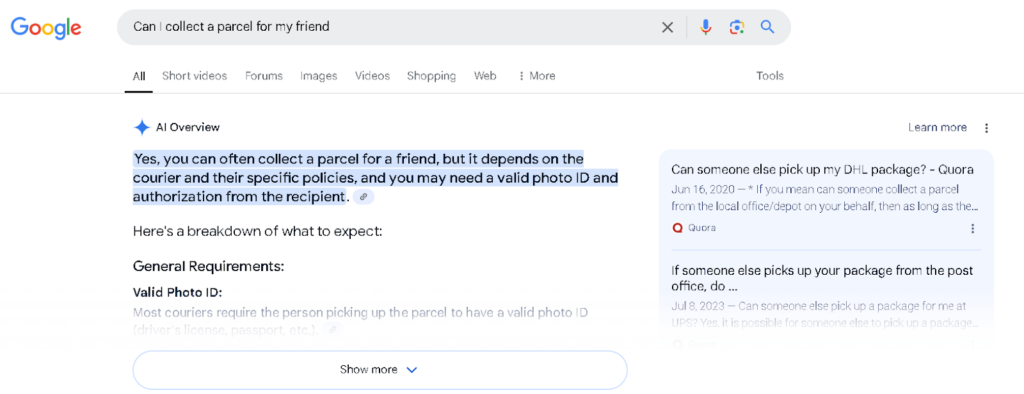
BERT stands for Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers. It might sound confusing, but trust us, this is a simple concept. BERT is merely a natural language processing model that works with long-tail searches.
Take this question: “Can I collect a parcel for my friend?” By using BERT, Google will figure out that you’re interested in getting someone else’s parcel. It won’t show you the locations of the nearby post offices, friends-related advice, or ideas for parcels — you’ll see the answers you’ve been looking for despite the complexity and length of your query.
Recommendations from Amazon
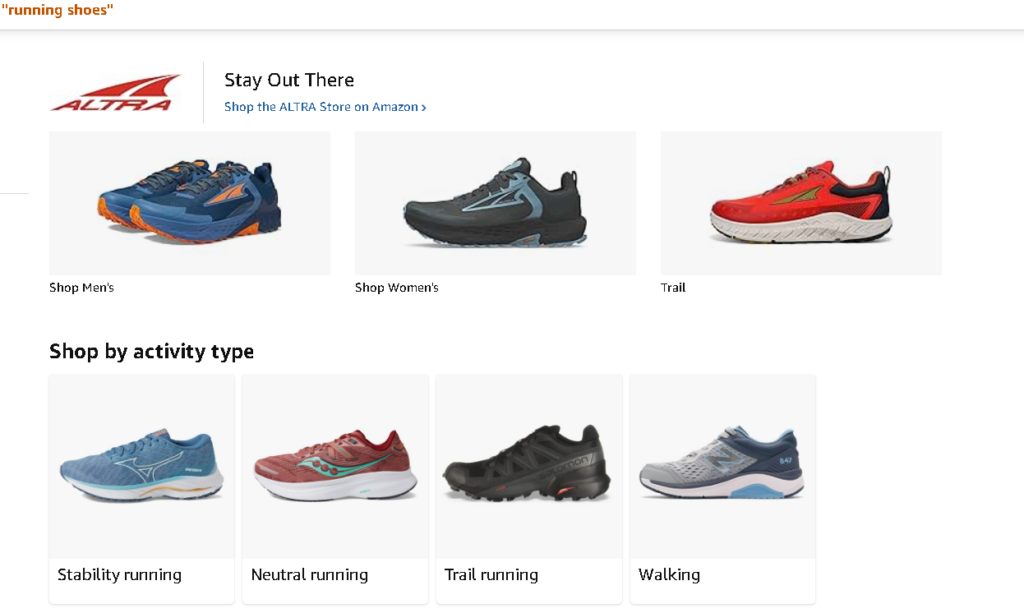
As soon as Amazon began to use semantic search in its operations, it started to thrive. Its recommendations are based on a complex semantic analysis: the Amazon search engine explores what kind of queries the user made before, what they reviewed, and which categories of products they’ve been clicking on lately.
If you type “running shoes” and there are New Balance products in your purchase history, Amazon will show you the latest releases from this brand. Its system of recommendations is precise, which is the result of a semantic search.
Siri, Alexa, and Other Voice Assistants
All AI helpers rely on semantic search to offer relevant responses to their owners. Their task is complex as they have to work with spoken language, which is often informal and not as clear as typed requests.
Once you ask, “What’s the weather?”, your AI assistant will use the NLP mechanisms and respond comprehensively. It won’t start talking about some random rains — you’ll learn about the current state of the weather in your specific location. This is possible thanks to a semantic search, which allows identifying intent and other specifics.
Other World-Famous Platforms
The recommendations you get from Netflix or YouTube, as well as platforms like eBay and Walmart, all fall into the same categories we’ve just discussed. They all use semantic search in their quest to meet their customers’ demands and return the most relevant and valuable answers to them.
Semantic Search vs. Keyword Search
All modern searches fall into semantic and keyword categories. They are both efficient and have similar basics, but the differences are more profound.
It’s time to consider their main features.
Semantic Search
Strengths
- Considers synonyms and intent behind the user’s request;
- Provides more specific and relevant search results;
- Interacts with the user by adapting to their behavior;
- Fully supports voice queries.
Weaknesses
- Might need more time as it’s based on advanced AI models, which require more processing power;
- Is less accurate when it comes to highly specialized spheres where each word has to be taken directly at its value.
There are definitely more benefits to semantic search than drawbacks, but there is some room for improvement, too. Importantly, website owners now have to work hard to refine their database performance because, otherwise, Google simply won’t rank their platforms highly. Quality content, texts that can be used as snippets, and other optimization techniques are a must for those who want to benefit from semantic search capabilities.
Keyword Search
Strengths
- Offers quick and straightforward results;
- Provides a high level of accuracy when responding to simple requests;
- Helps in situations where precise wording is vital.
Weaknesses
- Doesn’t do well with voice queries;
- Struggles with context and fails to decipher the nuances of natural language;
- Fails to respond to ambiguous requests properly.
Keyword search remains helpful, but only in specific situations. In the majority of cases, it is inefficient and frustrating, as it fails to supply the user with accuracy and keeps offering irrelevant results.
How Semantic Search Affects Website Optimization
All search engines are busy reorienting toward semantic search now. While keyword search remains useful, its helpfulness is losing its relevance year by year. Creating user-focused quality content is the best way to correspond to new standards and stay on top in terms of ranking.
We have already considered some examples, but now it’s important to evaluate how Google’s assessment system works and what you should do as a website owner to make your platform successful. There are three key metrics to pay attention to in your optimization process: quality, speed, and authority.
RankBrain: Quality Content
RankBrain is a product of Google that was rolled out back in 2015. It’s an AI system that is responsible for Google’s interaction with search results: RankBrain custom-tailors them and makes them unique enough to meet the needs of every individual person.
Remember us discussing that user intent is important? That’s because RankBrain prioritizes it. If you ask, “What is Starlink?,” you’ll get info on the product, the technology behind it, its creator, and the most popular way of its usage all at once because Google will strive to answer both what you asked and what you kept unvoiced.
Google responses have become highly comprehensive and rich in context, so your SEO strategy should focus on content quality improvement. Don’t resort to overwhelming your text with useless, distorted keys; add more substance instead.
If someone makes a strange and unfamiliar request, this system will nudge Google in the direction of the most similar queries. You can take advantage of this fact by adapting your content accordingly and taking new niches.
Features Snippets: Speedy Responses
Speed is the second aspect you’ll have to consider when optimizing your website content. Google favors platforms capable of providing quick and concise answers to users’ queries, and it uses Featured Snippets technology to achieve the best results.
These snippets are the short answers Google extracts from a selected website and shows on top. If you want your platform to be chosen, follow these tips:
- Provide direct answers to questions. Develop a FAQ section at the end of each page, or simply provide clear, concise answers to specific questions that your target audience might want to ask;
- Create comprehensive lists. Google loves lists, so offer step-by-step guides or share the steps a user might need to take to fulfill their goal;
- Present data in tables. Structure your data logically and present some of it in tables;
- Use questions as headers. To boost the chances of Google discovering your website, turn some of your headers into direct questions.
All these strategies will increase the possibility that a search engine will pick your website to quote from when addressing a user’s query.
E-A-T Principle: Degree of Authoritativeness
Authority is the third vital element of semantic search that has changed the rules of website optimization. E-A-T means expertise, authoritativeness, and trustworthiness. Your content has to correspond to all these criteria for your website to earn a promising ranking position.
Post content from reliable authors who have experience in a specific field. They should use credible sources to support their words and opinions — this will increase the website’s authoritativeness.
Update your content frequently, as it will help preserve its relevance. Mention the credentials of your selected author and enable readers’ reviews. Honest comments can make or break a website sometimes, and Google pays particularly close attention to this aspect.
Semantic search stands behind all these peculiarities, and the more of them you know, the easier it will be to optimize your website.

Incorporate Semantic Search into Your SEO Strategy
Now you know how drastically semantic search has changed the way Google evaluates websites. Platforms that used to be successful before have fallen from grace, and only those capable of meeting the evolving rules and standards have a shot at competing for top ranking spots.
Remember that the intent behind a user’s query matters most now. Tailor your content accordingly — offer something that you are sure your potential audience will want to learn about.
Do the voice search optimization. This will encourage Google to select your content when answering requests posed by Siri, Alexa, and other AI assistants. Use structured data and make quality your priority.
By using these simple tips, you’ll be able to appeal to your target audience and hold the first positions in Google. Stay up to date with all new semantic search trends, and you’ll never have to worry about staying relevant in online spaces.
