Digital information has transformed business operations, making data-driven strategies essential. Companies use advanced technologies to process large datasets, identify patterns, and improve efficiency. With growing computing and storage capacity, businesses can analyze more data for better insights into customer behavior, market trends, and operations.
Managing and using large datasets presents challenges. Businesses must ensure data accuracy, security, and accessibility while keeping pace with new technologies. Effective implementation requires a structured approach, including integration, governance, and analysis. Understanding best practices and key characteristics of data-driven processes helps organizations gain value and address potential issues.
What Is Big Data?
Big data refers to vast and complex datasets that go beyond the capabilities of traditional data processing tools like spreadsheets. It includes:
- Structured information, such as financial records or inventory databases;
- Unstructured content, like social media posts and videos;
- Mixed formats used for AI training.
These datasets can range from historical financial records to literary works, providing diverse sources for analysis.
Advancements in technology have lowered storage and computing costs, enabling businesses to store and access more data. This supports data-driven decisions but requires a strategic approach with skilled professionals to analyze patterns, ask relevant questions, and predict trends.
How Big Data Works
Big data provides deep insights that assist firms in discovering new possibilities and developing creative business models. The process consists of three primary steps: integrating data from many sources, managing it appropriately, and assessing it for meaningful insights.
Data Integration
Big data collects information from multiple sources, requiring more advanced methods than traditional extract, transform, and load (ETL) processes. Handling large datasets at the terabyte or petabyte level requires new technologies to organize and process data efficiently. The integration process involves gathering, processing, and structuring data so it can be used for analysis.
Data Management
Large datasets need a storage solution that can scale based on demand. Storage options include cloud-based, on-premises, or hybrid systems. The choice of storage depends on where the data originates and how it will be used. Data lakes are commonly used because they allow flexible storage and can adjust to different processing requirements.
Data Analysis
Analyzing big data provides useful insights for decision-making. Exploring data visually helps identify key information, while deeper analysis detects patterns and trends. Machine learning and AI models improve prediction accuracy and automate certain processes. Effective use of big data helps organizations improve efficiency, refine customer interactions, and support business growth.
The Five Key Characteristics of Big Data
Big data is traditionally defined by three main attributes—volume, velocity, and variety—known as the “Three Vs.” However, as data has become more integral to business success, two additional factors—value and veracity—have emerged, expanding the framework to the Five Vs of Big Data.
Many leading tech companies rely on data as a core asset, using it to drive efficiency, innovation, and competitive advantage. Understanding all five Vs is essential for making the most of big data.
- Volume – Involves processing large amounts of unstructured or low-density data, such as social media feeds, website clickstreams, and IoT sensor data, ranging from terabytes to petabytes;
- Velocity – Data is generated and processed at high speed, often in real time, requiring rapid analysis and action, especially for smart devices and internet-connected systems;
- Variety – Data comes in structured, semi-structured, and unstructured forms, including text, images, audio, and video, requiring preprocessing for meaningful insights;
- Veracity – Accuracy and reliability determine data quality. Ensuring integrity, consistency, and credibility is essential for making informed business decisions;
- Value – The true benefit of big data lies in extracting insights, optimizing operations, and enhancing customer engagement for business growth.
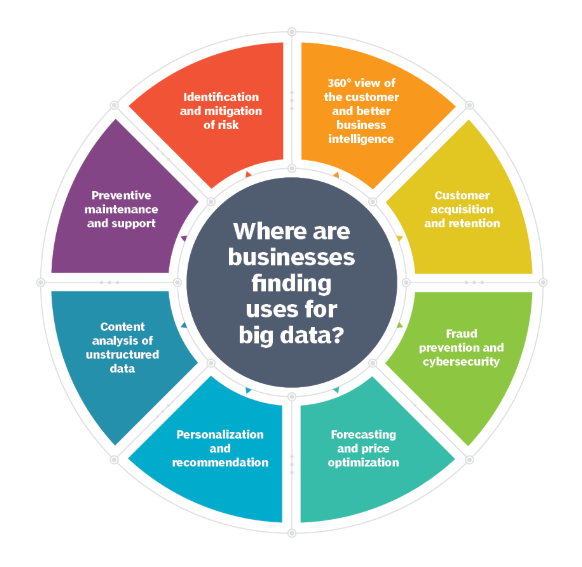
How Big Data is Transforming Industries
Big data is essential for simplifying corporate operations, increasing consumer experiences, and making better decisions. Here are some prominent sectors using big data to improve efficiency and innovation.
Retail and E-commerce
Companies like Netflix and Procter & Gamble utilize big data to forecast client demand and create new goods. They create prediction models for market performance by studying previous and present product qualities. P&G also uses focus groups, social media, test markets, and early retail rollouts to help enhance product development and launch tactics.
Companies apply online marketing strategies to use big data insights for customized advertising, consumer segmentation, and increased engagement.
Healthcare
Healthcare providers improve patient care and operational efficiency by merging internal data sources (e.g., electronic health records and wearable device data) with external inputs (insurance claims and medical research). This data-driven method optimizes staffing schedules, enhances supply chain management, and tailors treatment regimens to improve patient outcomes.
Financial Services
The banking industry uses big data to detect fraud, analyze risks, and maintain regulatory compliance. To satisfy changing compliance rules, financial institutions may analyze massive volumes of transaction data to detect suspect trends, avoid security breaches, and automate reporting processes.
Manufacturing
Predictive analytics helps manufacturers predict equipment failures by studying both structured data (machine specifications) and unstructured data (sensor readings, error logs, and performance indicators). This allows organizations to do preventative maintenance, reduce downtime, and increase the life of their equipment.
Government and Public Services
To improve public safety and resource allocation, government agencies gather and analyze data from a variety of sources, including traffic reports, emergency services, and public records. Data-driven model insights can optimize infrastructure development, enhance school budget distribution, and boost transparency by utilizing publicly available data.
The Advantages of Big Data
- Better Decision-Making: Managing and analyzing large data enables firms to detect trends and obtain insights, resulting in more informed operational and strategic choices;
- Faster Adaptation and Innovation: Real-time data analysis enables firms to react swiftly to market changes, improve manufacturing, and speed product development;
- Enhanced consumer Experiences: Combining structured and unstructured data allows for a more in-depth knowledge of consumer demands, which leads to greater personalization and service optimization;
- Ongoing data-driven insights: Automated real-time data streaming and sophisticated analytics enable firms to continually collect information, identify patterns, and discover new possibilities;
- Greater operational efficiency: Big data analytics may assist find cost-cutting opportunities, enhance procedures, and boost overall productivity;
- Stronger Risk Management: Analyzing massive datasets enhances risk assessment, allowing organizations to identify possible hazards earlier and increase mitigation techniques.
Challenges of Big Data
- Skilled Professional Shortage: Data scientists, analysts, and engineers are in great demand, and a lack of knowledge in handling and interpreting big data might impede growth. Businesses that lack the necessary abilities may find it difficult to extract useful information;
- Rapid Data Growth: Big data is always growing, and handling it without the proper processing, storage, networking, and security infrastructure may be burdensome;
- Concerns about data quality: Poor-quality data leads to untrustworthy analytics and poor decision-making. Raw data is frequently unstructured and has to be cleaned and organized to guarantee accuracy and relevance;
- Regulatory compliance: Because big data frequently contains sensitive information, firms must adhere to stringent data privacy and regulatory rules. Compliance with data localization and storage requirements is a continuous problem;
- Integration Difficulties: Many businesses store data in many systems, making it difficult to combine and utilize efficiently. Breaking down data silos and guaranteeing accessibility for business users is critical for extracting value from big data;
- Security Risks: Large databases include significant corporate and consumer information, making them potential targets for cyberattacks. Their intricacy makes it difficult to apply consistent security measures.
Addressing these challenges requires a combination of the right talent, strong infrastructure, proper data governance, and advanced security measures to ensure big data is managed effectively and delivers real value.
Best Practices for Managing Big Data
Implementing big data effectively requires strategic planning and structured processes. Here are key practices to ensure a solid foundation for big data management.
Align Data Initiatives with Business Objectives
Large datasets provide valuable insights, but data projects should always align with business goals. Investments in skills, infrastructure, and technologies should be guided by business priorities to ensure continued support and funding. For example, businesses may use big data to analyze eCommerce behaviors, track customer sentiment, or apply statistical methods to improve operations across various departments.
Address Skill Gaps Through Standardization and Training
A common challenge in big data adoption is the lack of skilled personnel. Organizations can mitigate this by integrating big data management into IT governance, standardizing approaches, and regularly assessing skill requirements. Training existing staff, hiring specialized talent, or working with external consultants can help bridge knowledge gaps.
Establish a Centralized Knowledge Hub
Creating a center of excellence helps organizations manage big data resources more efficiently. This approach allows teams to share insights, improve oversight, and enhance communication. Whether big data is a new initiative or an expanding investment, centralizing expertise ensures that costs and resources are managed effectively across the organization.
Combine Structured and Unstructured Data
Analyzing unstructured data on its own is valuable, but combining it with structured data improves business knowledge. Combining information, such as consumer feedback and transactional data, yields richer insights. Businesses may improve analytics by connecting many data sources, resulting in more exact findings.
Using the best BI tools enables organizations to connect structured and unstructured data, making it simpler to evaluate trends, spot patterns, and make better decisions.
Support Data Exploration and Experimentation
Extracting meaningful insights from big data often involves trial and error. Data teams need the flexibility to explore datasets and test statistical models without rigid constraints. Creating well-supported sandbox environments allows analysts and data scientists to experiment while maintaining governance over data use.
Use Cloud Resources for Scalability
Big data workflows require flexible infrastructure to handle both experimental analysis and large-scale production tasks. Cloud-based solutions provide scalable storage and computing resources, enabling efficient data integration, modeling, and analytics. A well-planned cloud strategy helps organizations manage security, data provisioning, and performance optimization effectively.
Following these best practices helps businesses maximize the potential of big data, ensuring efficient management, deeper insights, and better decision-making.
Big Data Strategies and Solutions
Creating an effective data strategy begins with establishing corporate objectives, finding use cases, and evaluating accessible data. Organizations must also assess if more data or new technologies are required to achieve their goals.
Unlike traditional data management, big data solutions handle large, complex datasets to improve analysis and decision-making. These tools manage data volume, processing speed, and diverse data formats.
There is no universal approach to big data. Each organization must tailor its strategy based on its specific needs. The following key concepts can help businesses build a successful big data framework:
- Open: Big data systems should be adaptable, allowing organizations to integrate multiple tools, open-source technologies, and cloud platforms. As data sources expand and new innovations emerge, flexible architectures help businesses collect, process, and analyze data more efficiently;
- Intelligent: Using AI, machine learning, and automated analytics can improve big data operations, increasing efficiency and supporting better decision-making. Self-service analytics tools enable employees to access and analyze data independently, reducing reliance on technical teams;
- Flexible: Big data solutions should support business growth rather than restrict it. Organizations need scalable computing and storage resources, unified data access, and the ability to integrate different technologies to fit specific workloads and use cases;
- Trusted: Data security and reliability are critical for retaining confidence. Built-in security measures must be implemented by organizations to assure data accuracy, relevance, and protection. Compliance, redundancy, and secure storage solutions are critical to ensuring data integrity.
Conclusion
Big data is a key part of business operations, helping organizations analyze large datasets, track trends, and improve decision-making. It is used across industries for customer insights, operational efficiency, fraud detection, and public services. Effective management requires integration, security, and analytics. Businesses must ensure data accuracy, implement security measures, and use scalable storage. As AI, machine learning, and cloud computing evolve, companies must adapt to keep data useful. A clear big data strategy supports better decisions, improves efficiency, and helps businesses stay competitive.
